A poor Wi-Fi signal on your Nintendo Switch isn’t any less than a nightmare. Lag, unreliable connections, and slow downloads are frustrating and no doubt worsen your gaming experience. Wi-Fi problems aren’t rare with the Nintendo Switch, but thankfully they’re usually pretty easy to resolve.
A bad Wi-Fi signal on a Nintendo Switch is usually caused by a temporary outage from the Service Provider, but it can also be from weak Wi-Fi signal or a crowded Wi-Fi network. Switch to a 5GHz band, if you have one. Repositioning the router and/or restarting everything is a good next step.
Just as there are multiple causes for bad Wi-Fi signals on a Switch, there are multiple solutions. If you want to stabilize your internet and enjoy smoother gaming, you are in the right place. So, let’s get started!
Why Is Your Wi-Fi So Slow on Your Nintendo Switch?

What a loaded question right? There are so many possibilities here, and we’ll dive into them below. Real quick, though, take note of the other resource we have around Nintendo Switch connectivity, like how to use your console on a 5GHz WiFi network to increase download speeds and decrease lag, as well as how to handle a Switch that won’t connect to WiFi at all. Now, back to figuring out why you’re having a poor Switch WiFi experience right now.
Wi-Fi Device (Moden/Router) Problems
Are you sure that your Wi-Fi device isn’t behind the slow connection on your Nintendo Switch? Your console might not be to blame. The issue might lie with your internet service provider (ISP) or the Wi-Fi device itself.
For this reason, it’s important to check if your other household gadgets are having internet connectivity issues first.
Before you troubleshoot issues with your console, check the Wi-Fi speed on another device like your mobile phone or laptop. If the internet is working properly on your other electronics, then your Wi-Fi device might not be the culprit.
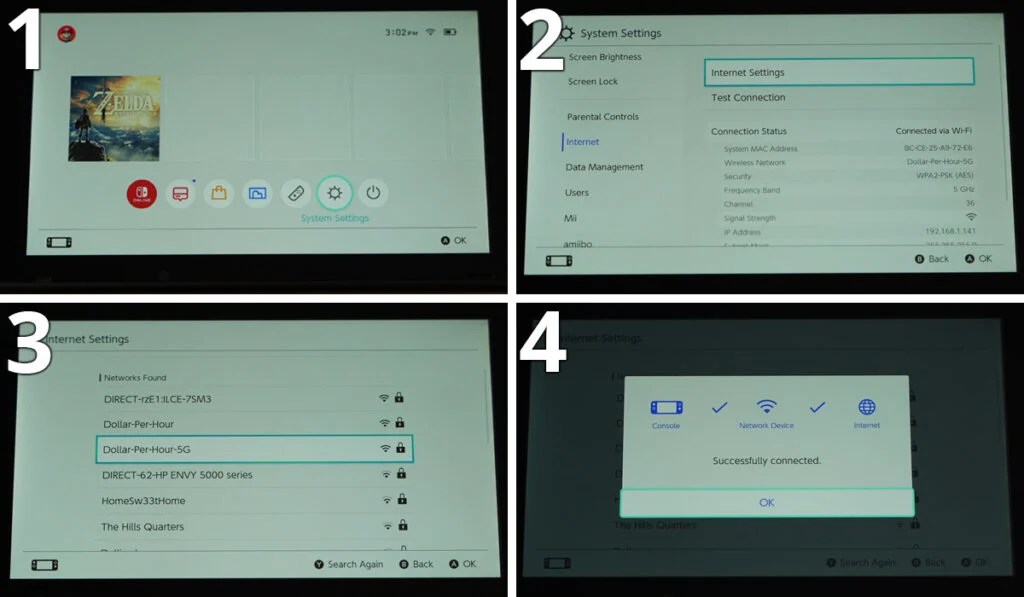
You can check if there is an issue with your ISP by performing a connection test on your Nintendo Switch. Follow the steps below:
- Go to the “System Settings” from the Home menu.
- Select “Internet” from the System Settings menu.
- Click on “Test Connections” and wait for the result to show up.
- Take notes for both “Download Speed” and “Upload Speed” from the results.
The ideal speed for downloading on a Nintendo Switch is 3 Mbps, and the ideal speed for uploading is 1 Mbps.
Location of Router or Wi-Fi Modem
Placing your router or modem too far away from your Nintendo Switch can result in a slow internet connection.
If you are using your console in a room far away from the router, walls and other barriers between the two devices can cause a slow internet connection. Building materials like concrete, plaster, metal, steel, and so on can block the Wi-Fi signal from reaching your console.
Other materials that can disrupt the Wi-Fi signals include:
- Metal Lath
- Ceramic Tiles
- Tinted Glass
- Mirrors
As a rule of thumb, if your router is more than 30 feet away from your console, expect a slower internet connection. The closer your console is to your router, the better the internet connection.
Other Devices Are Using the Same Frequency
A Nintendo Switch supports two Wi-Fi frequencies: 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. Devices that use the same frequency as your Nintendo Switch can block out or slow down the Wi-Fi signal.
This means that other electronics like baby monitors, cordless phones, microwaves, and wireless security cameras can slow down your Nintendo Switch. It’s best to use your Nintendo Switch away from these devices.
If you have to make a phone call in close proximity to your Nintendo Switch without disrupting the Wi-Fi signal in it, go for a wired phone. You can get one like the AT&T Advanced American Telephone (on Amazon).
Neighbor’s Wi-Fi Network (Interference)
When you open the Wi-Fi menu on your console, you can see the names of multiple nearby Wi-Fi devices, like your neighbors’. If your Wi-Fi router is placed where a neighbor’s Wi-Fi signals can overlap or disturb your Wi-Fi signals, it might cause a slow connection.
Multiple Devices Using the Same Wi-Fi (Lack of Bandwidth)
If other household members use the same Wi-Fi as your console to stream video through services like Netflix and YouTube, it can cause a slow connection on your Switch.
One or two people scrolling through social media on the same network shouldn’t be much of a problem, depending on the quality of your internet service. But things like video and music streaming, downloading apps, and online gaming can use a considerable amount of bandwidth. Therefore, they can disrupt the internet signals in your console.
Nintendo Switch Software Glitch
Sometimes it isn’t the Wi-Fi that is causing slow internet speeds on your console. Software bugs in Nintendo consoles can cause the following Wi-Fi issues:
- Randomly disconnecting Wi-Fi
- Slow internet
- Inability to connect to the internet
- Wi-Fi signal interference
Such issues are temporary, so you don’t need to worry too much about them. A simple factory reset or restarting the Nintendo Switch can solve this issue.
Hardware Issues in Your Nintendo Switch
Hardware malfunctions are a rare cause of bad Wi-Fi on your console. Because it’s so uncommon, make sure you work through the above fixes before assuming the worst.
When in doubt, restart your console. If the issue persists, you might need to repair it. Sometimes hardware malfunctions are unfixable, requiring you to replace your console. Again, a hardware malfunction like that is rare, so replacing your console is a last resort.
How Can You Make Your Nintendo Switch Wi-Fi Faster?
Before blaming your Switch, make sure that your Wi-Fi router isn’t the cause of your internet woes. If that doesn’t work, then try speeding up the Wi-Fi through your console.
Troubleshooting Problems With Your Wi-Fi Devices
First, do an internet connection test on your Nintendo Switch to determine your Wi-Fi’s download and upload speeds. If you find that the speed is slow, you can try:
- Restarting your router
- Resetting your router
Sometimes restarting the router makes the signals strong again, returning your Wi-Fi’s speed back to normal. If restarting doesn’t help and you are sure that the problem comes from your Wi-Fi, then you can reset the device and make sure that it is up-to-date.
If these two options don’t help, then there might an issue from the backend. Call your internet service provider and ask them to check for problems with your Wi-Fi.
Power Cycle Your Router
It’s best to start by power cycling your router. “Power cycling” might sound like something technical and difficult, but it is as simple as restarting your router — AKA “turning it off and turning it on again.”
To perform a power cycle for your router, turn off the device and leave it alone for at least 30 seconds. Turn it on again after 30 seconds and your power cycle is done.
Reposition Your Console and Router
The position of your router and console matters a lot if you want a stable internet connection.
As a rule of thumb, don’t place your router in a place where other signals can disrupt the Wi-Fi. Choose a room where there are as few other Wi-Fi connections (like the ones from neighboring houses) as possible.
The next thing to remember is to place your console as close to the router as you can. If there are no barriers between the console and the router, the signal will be stable and the internet will work faster.
Ideally, place your console and router in the same room so that barriers like concrete walls, steel bars, and windows can’t disturb the internet connection on your console.
Devices with the same Wi-Fi frequency also shouldn’t be used near the console. So, make sure that the room where you play on your Nintendo Switch doesn’t contain any devices that use the same frequency.
Switch Your Router’s Frequency
Your Wi-Fi router can operate using one of two frequencies: 2.4 GHz or 5GHz. One major issue with the 2.4 GHz signal is that many common household devices use this frequency. Multiple devices using the same frequency can cancel out each other’s signals, including the one on your Switch.
Changing your router’s frequency to 5 GHz will not only provide a faster internet service, but also a more reliable connection.
Use Wi-Fi Repeaters
A Wi-Fi repeater or range extender brings Wi-Fi signals to places where they don’t normally reach. Wi-Fi signals can be disrupted by barriers, and range extenders can handle this issue.
You might have blind spots in your home where the Wi-Fi signals are weak or simply don’t reach you. If it happens to be in the spot where you want to use your console, then a Wi-Fi range extender might do the trick.
Range extenders are best for big places with a lot of range that a single router can’t handle. You can get one like the TP-Link AC 12000 Range Extender (on Amazon).
Use a Wired Connection
Another option is to forgo using a wireless connection altogether. Instead of using a wireless internet connection, you can establish a wired connection using an ethernet cable.
LAN adapters connect to the console directly using a wire called a USB to ethernet adapter, like the TP-Link USB to Ethernet Adapter (on Amazon). It not only supports the Nintendo Switch but other devices as well, including laptops and Macbooks.
To connect your Nintendo Switch to your router through an ethernet adapter, connect the USB port to your Nintendo’s port. Connect the other part of your device to the router (usually at the back). Then go to your Nintendo Switch’s settings and select “wired connection” instead of Wi-Fi.
You will notice a huge difference in the performance of your internet when you use an ethernet cable. This is because there are no barriers and only a single device is connected to the router. The internet comes directly through the wire, providing a strong signal.
Use a Powerline Adapter
Powerline adapters can help you have a wired connection similar to an ethernet cable. The benefit of using a powerline adapter is that it can be extended anywhere in your house and you don’t have to sit by the router to use your console. We recommend the NETGEAR Powerline Adapter Kit (on Amazon).
How to Speed Up Your Wi-Fi Signal Through Your Switch
This is a bit more advanced of an option, so if you’re not comfortable changing these settings, it may be best to re-try some of the options above. That said, following the steps below may get you some relief here if nothing else has.
DNS Settings
Changing your domain name system (DNS) can enhance the speed of your internet to a shocking extent. You can change your domain to a better one at no charge. This is especially useful when the default DNS from your internet provider isn’t the best.
You can opt for the DNS provided by Google. To do so, follow the steps below on your Nintendo Switch:
- From the “Settings” menu, select “Internet,” then “Internet Settings.”
- Select your network from the list.
- From “Change Settings,” select “DNS Settings.”
- Select “Manual.”
- Under “Primary DNS,” enter “8.8.8.8”.
- Under “Secondary DNS,” enter “8.8.4.4”.
Now you’ll notice a huge difference in your internet speed because Google’s DNS server ensures that the internet is well-working.
Change the Maximum Transmission Unit
You can expect a solid improvement in your internet speed on your console by changing the your maximum transmission unit (MTU). Changing the MTU will enable the Switch to transfer and receive more data at a time.
To do this, follow the steps below on your Nintendo Switch:
- From the “Settings” menu, select “Internet,” then “Internet Settings.”
- Select your network from the list, then “Change Settings.”
- Select MTU and change the number to 1500 from 1400.
- Select “Save.”
If your MTU setting is already set to 1500, then you can’t go higher than this. But, by changing the MTU, you can increase the size of your data packet by approximately 6.6%, a satisfactory improvement.
Connect Your Switch to 5 GHz Wi-Fi
A Nintendo Switch allows you to connect to both 5 GHz and 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi. As we mentioned before, a 5 GHz Wi-Fi is not only more reliable, but faster.
After switching to 5 GHz, you’ll notice a day and night difference in your gaming experience when you use your Nintendo Switch. This is because the 5 GHz frequency is used left often by other electronics, and most of the other devices around you only use the 2.4 GHz signal.
One setback of using a 5 GHz signal is its shorter range. You might have to sit in the same room as your router or as close as possible to it for a better signal. And of course, your Wi-Fi router has to support the 5 GHz frequency in order to get the benefits of it.
